Do you need an air barrier or a vapor barrier? This is a heavily debated topic in building science. In this post, we’ll outline the basics and put forth our view to help you make an informed decision.
We Recommend a Vapor Open Air Barrier
First a very basic overview of each type of barrier. A VAPOR barrier is designed to prevent the diffusion of vapor (water molecules in the air) through a home’s wall assembly. Different materials will have different degrees of vapor permeability, that is the material’s ability to allow water vapor to pass through it. Simple physics dictates that moisture flows from an area of higher concentration towards an area of lower concentration of moisture, or from a warmer to a cooler space within a building material. Real-life example: over the course of one heating season a third of a quart of water will diffuse through an 8’ x4’ section of drywall. A vapor barrier is designed to prevent this.
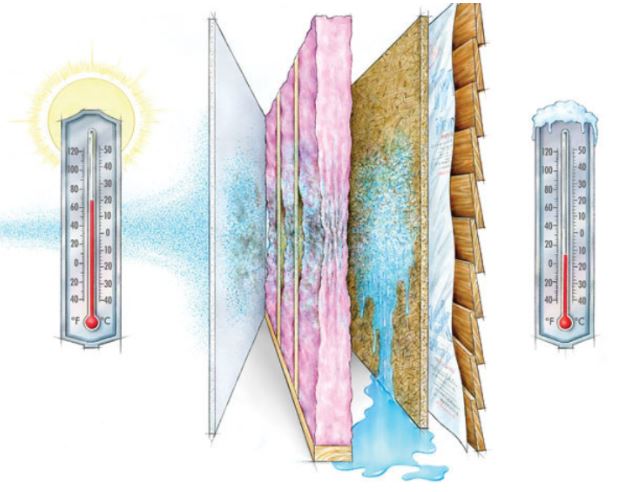
An AIR barrier blocks the flow of air from entering a wall assembly… think airtightness. Using the above example of drywall, 30 quarts of water will move through based just on air leakage (roughly speaking the amount of moisture carried by airflow is 50 to 100 times greater than that carried by vapor diffusion). Hence a commonly accepted maxim in building science – restricting air movement is more important than vapor when it comes to preventing moisture leaking into a wall assembly.
What is a Vapor Open Air Barrier?
Let’s start with a basic premise. Moisture will get into your walls, one way or another. And when it’s in your walls you definitely don’t want to trap it, a risk with an (impermeable) vapor barrier (or retarder). Traditional insulation does not handle moisture well (mold, mildew) so a vapor closed strategy seems sensible but when vapor inevitably finds its way in and can’t escape, bad things happen. Through a myriad of specialized materials and sometimes flawed practices, the building science consensus is now to allow vapor an escape path so assemblies can dry out either inward, outward, or both. Walls don’t need to breathe but they do need to dry.
So we need an air barrier that also allows for moisture management (vapor variable). It should remain tight in winter when humidity in the cavity is low to prevent moisture from entering but also needs to increase permeability in summer to let moisture escape, helping to keep the wall dry. Hence a Vapor Variable Barrier or also referred to as Smart Air Barrier.
Where do I put this Air Barrier?
There are options. An external air barrier is useful in cutting air penetration off at the source – think wind shear. Additionally, an air barrier can be placed inboard of the insulation. An ideal scenario is arguably both; however, from our perspective, it is best to control air on the exterior, put wool in your walls and allow it to do what it does best – manage inevitable moisture.
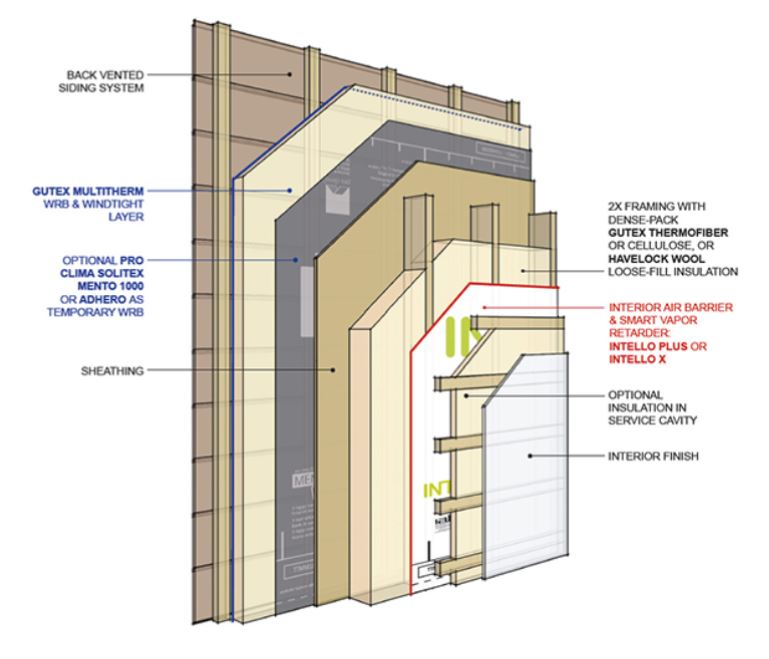
There are very smart people out there with varying opinions so in the end be diligent, gather multiple opinions and as ever make an informed decision that suits you and your climate best.

Cost. Might be far to costly to be accessible to most home buyers
Good info for everyone to know. Great graphics.
With what I’m reading this sounds like a good solution to subterranean block walls that have been fired for drywall…the one I’m trying to insulate is framed with a space behind?
Thanks for the “plain English” version of this. Trying to sort out the vocabulary and then what it means in practical terms for one’s house or other building is a challenge. This was very useful information!
Thank you for this excellent explanation of the air barrier issue and how it can be solved.
Great rundown.
As an insulation contractor through the nineties, this was discussed a lot and codes were all over the place. Here in Idaho we have to be prepared for extremes in temperatures from -20F to 110F in the valleys, subtract about 10-20F from each in the mountains. Fortunately our humidity is seldom high here.
This was also my consensus at the time after doing much research: make the outside of your exterior walls deal with whatever extremes of weather are common in your area, use good insulation (almost anything besides fiberglass!) and don’t worry about interior vapor barriers, two coats of latex paint is about as impervious as you need.
The topic of air vs vapor barrier is a good one. Personally and professionally I like air to travel through the assembly to some extent just so the house breathes and promotes healthier indoor air quality naturally, passively, without mechanical air exchangers. Even today many new builds aren’t engineering for that air exchange and sick building syndrome is still rampant even in brand new homes.
What’s missing from this post is discussion of dew point – the moment when water vapor condenses and becomes water droplets that puddle and cause issues. The assembly in the graphic above is a little more complicated than it needs to be to solve the problem, and this in turn drives cost of construction up, both in material and labor cost. A more straightforward approach is to design the wall assembly so that the dew point happens outside the structure and sheathing layer. By using “outsulation” rather than “insulation” and placing enough R-factor material like insulation sheets or straw bales outside the wall then the dew point happens outside of the drainage plane so it doesn’t matter if vapor or air travels through the assembly.
Then go ahead and infill the stud cavity with wool for extra warmth and comfort, but let the dew point happen outside the sheathing with a drainage plane between sheathing and siding and “outsulation” boards or bales for drainage.
Love using natural wool! Great advice.
DuPonts’ Tyvek HomeWrap is vapor permeable but a barrier to air & liquid-water. With a pressure treated baseplate, sill plate gasket, and exterior siding/cladding, most of your moisture problems are solved. Make sure you use vapor permeable paint on your drywall (e.g. latex paint). By using wool insulation you have the added advantage of an insulation that passively handles changes in humidity. Some people also install furring strips to increase airflow & therefore drying between the exterior cladding and their vapor barrier.