As our business grows we meet more people everyday interested in healthy building.
Some are building experts but often people are just beginning to learn how homes are built. With all the jargon and terminology out there, it can be intimidating to even start a conversation, especially when it comes to insulation.
With that in mind, we put together our list of key insulation terms. It is not exhaustive but with just a little background knowledge, the complexities of the built environment and insulation, in particular, will be much simpler. And this will help everyone make more informed decisions.
Take a read below and please let us know any feedback!
Insulation Terms
R-value is the resistance value of the insulation i.e. the limiting factor for thermal conductivity. The higher the number the more insulated the space.
Thermal bridging is when outside temperatures are conducted inside and vice versa. Think of a structural metal beam that runs from the outside, in. When that beam transports cold air to the inside of the structure – that is thermal bridging.
Air-tightness is an increasingly measured element in building. An air-tight structure is considered more efficient. Often it is.
A convective loop is the cycle of air inside a room resulting in heat loss. Warm air rises, cold air flows downward.
Wind washing is when wind drive blows air through walls and insulation. Not only can this make your home cold (or hot) but it can also cause condensation.
Vapor drive diffuses moisture vapor into and through walls which causes condensation. It can move from outside to inside a house or inside to outside.
Types of Insulation
Batts are precut insulation designed to fit into specific cavities.
Loose-fill is a blown application generally seen to reduce the potential for gaps in cavities.
Facing is a covering applied to one side of insulation. Popular with fiberglass… not necessary for wool.
A vapor barrier is any material (typically a poly film) used to resist the diffusion of moisture (or vapor drive… see above!)
Insulation Metrics
R-Value (again) measures insulation’s resistance to heat flow. As R-value increases, the better the insulation resists the transfer of heat.
Flame spread and smoke development measure resistance to flame and how much smoke is developed. Most insulation conforms to Class A of the building code by adding various chemicals. Wool does it naturally.
Sound transmission coefficient (STC) is a rating scale used to measure the sound rating or deadening ability of a wall.
Noise reduction coefficient (NRC) is similar to an STC except that it measures a material’s sound attenuation characteristics….versus a wall system which can have multiple components.
WUFI is the measure of an insulations ability to manage moisture.
Building Terms… and some diagrams
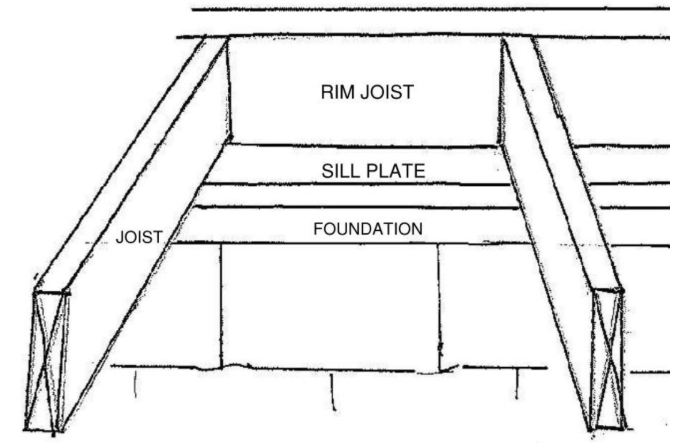
Joists are lengths of timber (or steel,etc) arranged in parallel to support floors or ceilings.
Studs are vertical framing pieces, usually wood and typically 2×4 or 2×6.
Furring strips are wood or other material used to level a surface to which insulation can be attached.
Rim joists attach perpendicularly to the joists providing support for the ends of the joists while capping off the end of the floor.
On Center (O/C) is the measurement from the center of one stud to the center of another stud.
Eaves are the part of the roof that overhangs a wall.
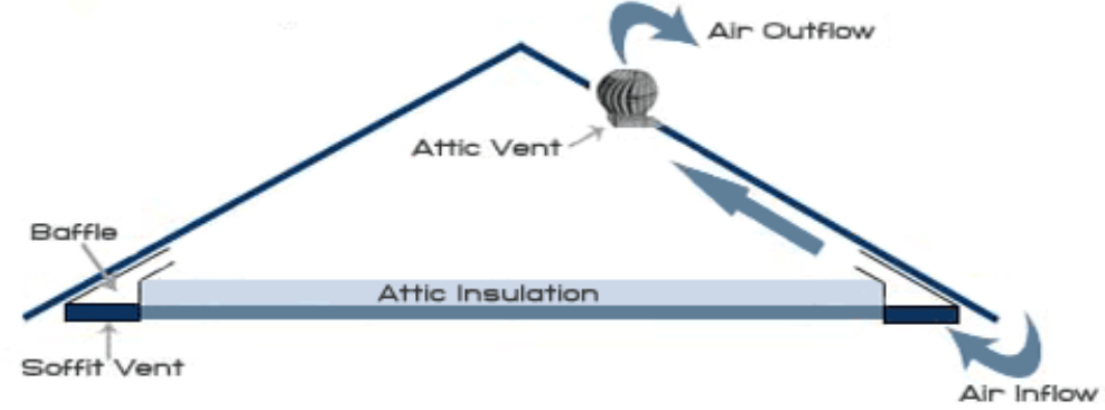
Soffit vents are vents in a soffit (underside of an eave) that allows fresh air into an attic.
Baffles are chutes that channel from soffit vents into attic space. This helps reduce moisture in your attic.
Attic vents are placed on a roof to allow air flow.
A ridge vent is installed at the peak of a roof to allow air flow in an attic.

Hello, I am writing from Cols, Ohio. I am wondering if havelock wool can and/or should be used to insulate rim joists (in the basement)? Thanks, Jenny Morgan
Hi Jenny – Yes, Havelock Wool will work in that application. Email us at sales@havelockwool.com with more details on your project and we can help. Thanks for reaching out!